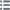
Лицевая сторона
Аверс: легенда: [TI. CAES]AR. AVGVSTI. - F. IMPERATOR. V..
Аверс: описание: Tête laurée de Tibère à droite (O*).
Аверс: перевод: “Tiberius Cæsar Augusti Filius Imperator quintum”, (Tibère césar fils d’Auguste revêtu de la cinquième acclamation impériale.
Обратная сторона
Реверс: легенда: ROM ET AVG.
Реверс: Описание: Autel de Lyon.
Реверс: перевод: “Romæ et Augusti”, (À Rome et Auguste).
Комментарий
Историческая справка
LUGDUNUM - LYON - TIBERIUS
(08/19/14-03/16/37
Caesar
Lyon, colony "Copia Felix Munatia Lugdunum" was founded in 43 BC. -VS. by Lucius Munatius Plancus, one of Caesar's and then Antony's lieutenants. The colony seems to have received the "jus Romanum". This coinage is reminiscent of those of Orange, Narbonne, Vienne and finally Nîmes. August 1, 12 BC. -VS. , at a place called Condate, at the confluence of the Rhône and the Saône was founded the federal sanctuary of the Three Gauls intended to commemorate the religious and political union of the provinces conquered with Rome and Augustus. This sanctuary was located at the current site of the Croix-Rousse. The monument was presented as a vast terrace above which rose a monumental altar bearing the name of the sixty Gallic cities of the Three Gauls (Aquitaine, Lyonnaise and Belgium). The altar was adorned with statues symbolizing the cities. On each side of the altar rose a column surmounted by a bronze victory. The coinage at the altar of Lyon continued to be made under Tiberius and until Claude who struck the last aces and semis.. Claude, son of Drusus and Antonia and brother of Germanicus, was born in Lyon on August 1, 10 BC.. -VS. , two years after the inauguration of the Altar of the Three Gauls. He remained favorable to the Gauls when he became emperor and brought them into the Senate in 48 (see Claudian Tables, preserved in Lyon and compare them to the recension given by Tacitus, Annales, XI, 23-25). The imperial workshop in Lyon, which had been opened by Augustus around 15 BC. -VS. , was the main mint of the Empire until the death of Caligula and remained important during the reigns of Claudius and Nero until the Monetary Reformation of 64. Until that date, it was the only mint to manufacture aurei and denarii. The reform withdrew the manufacture of precious metal species, but kept those of bronze (very important). It was in fact the fall of the emperor in 68, then the civil wars which followed between 68 and 70, which modified the status of the imperial workshop.. The rebirth of a "Gallic" particularism and the ephemeral "Gallic Empire", proclaimed by Civilis, the Batavian, joined by Julius Tutor and Julius Classicus, both Treveri and Julius Sabinus of Lingon, were to cause a reaction from Rome. Vespasian, the new emperor, sent Q. Petillius Cerialis in Gaul to crush sedition. The Gauls were defeated on the Moselle and the conspirators then experienced various fates. Gaul had returned to obedience to Rome. The Lyon workshop closed its doors definitively in 78 for a long time, putting an end to Gallic particularism. We must now modify our interpretation of the monetary circulation in Gaul between the end of the Gallic Wars and the death of Nero.. Gallic coins in silver, bronze and pewter circulated together with Roman coins which slowly spread outside Narbonnaise. It is necessary here to evoke the neologism of "Roman-Gallic" circulation rather than Gallo-Roman.








 Cообщить об ошибке
Cообщить об ошибке Распечатать страницу
Распечатать страницу Отправить мой выбор
Отправить мой выбор Задать вопрос
Задать вопрос Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Информация
Информация