fme_374090 - SECOND EMPIRE Médaille de la paix de Paris
недоступный.
Товар уже продан в нашем интернет-магазине (2016)
Цена: : 300.00 €
Товар уже продан в нашем интернет-магазине (2016)
Цена: : 300.00 €
Тип Médaille de la paix de Paris
Дата: 1856
Монетный двор / Город: Paris
Металл: copper
Диаметр: 75,5 mm
Ориентация осей монеты: 12 h.
Гравер BOVY Antoine (1795-1877)
Вес: 199 g.
Век: lisse + main CUIVRE
Комментарии о состоянии
Splendide médaille, en excellent état et de très bon style, avec une belle et homogène patine brune. Un léger coup sur la tranche est à signaler à 10 heures au droit
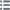
Лицевая сторона
Аверс: легенда: NAPOLÉON III EMPEREUR.
Аверс: описание: Tête nue de Napoléon III à gauche.
Обратная сторона
Реверс: легенда: PAIX DE PARIS, 30 MARS 1856. // LE COMTE WALEWSKI / PRÉSIDENT DU CONGRÈS.
Реверс: Описание: Cinq allégories faisant la paix devant un autel orné des armes de Paris.
Комментарий
Le traité de Paris du 30 mars 1856 met fin à la guerre de Crimée (1853-1856). Entré en vigueur le 16 avril 1856, il déclare la neutralité de la mer Noire, y interdit la navigation aux navires de guerre ainsi que la construction de fortifications. Il marque le début d'un sévère déclin de l'influence russe dans la région.
Alexandre Florian Joseph Colonna, comte Walewski, né le 4 mai 1810 au château de Walewice (Pologne) et mort le 27 septembre 1868 à Strasbourg, est un homme politique franco-polonais, particulièrement connu pour être le fils naturel de Napoléon Ier..
Alexandre Florian Joseph Colonna, comte Walewski, né le 4 mai 1810 au château de Walewice (Pologne) et mort le 27 septembre 1868 à Strasbourg, est un homme politique franco-polonais, particulièrement connu pour être le fils naturel de Napoléon Ier..








 Cообщить об ошибке
Cообщить об ошибке Распечатать страницу
Распечатать страницу Отправить мой выбор
Отправить мой выбор Задать вопрос
Задать вопрос Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Информация
Информация



