Назад 1/1
E-auction 27-8843 - fjt_01780 - DIJON (MAIRES DE ... et divers) François Malateste 1652
Чтобы принять участие в торгах, вы должны войти в систему и стать подтвержденным участником аукциона. Войдите, чтобы сделать ставку. Ваш аккаунт будет подтвержден в течение 48 часов. Не ждите до закрытия торгов, чтобы зарегистрироваться.Сделав ставку на данный товар, вы вступаете в юридическое соглашение на покупку выбранного товара и нажатием кнопки «Сделать ставку» подтверждаете принятие вами условий интернет-аукционов cgb.fr.
Ставка может бить сделана только в полном эквиваленте евро. Торги закроются согласно времени, указанному в описании товара, все ставки, сделанные после закрытия торгов, учитываться не будут. Не следует откладывать предложение вашей ставки до последнего момента, так как система может не успеть обработать вашу заявку, и ваша ставка не будет принята. Более детальную информацию вы найдёте здесь: FAQ по интернет-аукционам.
БЕСПЛАТНО.
БЕСПЛАТНО.
| Оценить : | 45 € |
| Цена : | 7 € |
| Максимальная предлагаемая цена : | 9 € |
| Конец торгов : | 21 October 2013 18:21:00 |
| Участников : | 4 Участников |
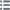
Тип François Malateste
Дата: 1652
Металл: red copper
Диаметр: 27,4 mm
Ориентация осей монеты: 6 h.
Век: lisse
Редкость: R1
Ссылки в каталоге: :
Лицевая сторона
Аверс: легенда: VICIT. AMOR. PATRIAE. 1652.
Аверс: описание: Armes de Maleteste : de gueules à une face d'or accompagnée en chef d'une fleur de lys d'or et en pointe d'un croissant d'argent.
Аверс: перевод: L'Amour pour sa patrie est vainqueur - 1652.
Обратная сторона
Реверс: легенда: FR. MALETESTE. ADV. EN. PARL. VIC. MAIEUR. DE. DIION.
Реверс: Описание: Armes de Dijon.
Комментарий
François Malateste était l’avocat du duc d’Épernon alors gouverneur. Il fut désigné par Millotet, son prédécesseur, qu’on voulait réélire mais qui avait été prié par le duc d’Épernon de ne pas accepter attendu que celui-ci avait promis à M. le prince qui n'aimait pas Millotet qu'il n'accepterait pas. Il porte de gueules à une face d’or accompagnée en chef d’une fleur de lys d’or et en pointe d’un croissant d’argent. La devise du revers est tirée de l’Énéide de Virgile
Les maires de Dijon
Dès l’époque de la naissance de la féodalité, la ville de Dijon possédait un maire et en général vingt magistrats municipaux, ou échevins. Ces magistrats sont confirmés en 1187, lorsqu’une charte de commune est accordée par le duc Hugues III. En 1192, pour la première fois, le maire dijonnais est élu.
A la fin du XIIIe siècle, ce maire prend le titre de vicomte maïeur, confirmé en 1477-1479 par Louis XI, qu’il gardera jusqu’en 1789. Depuis la fin du XVe siècle (1491), la charge de vicomte maïeur est anoblissante ainsi que celle d’échevin à compter du XVIe siècle. Le vicomte maïeur avait le droit de haute, moyenne et basse justice, le droit de scel et de visite. Les clefs de la ville lui sont confiées et il dirige les archers ainsi que les compagnies des sept quartiers, cette fonction militaire étant importante jusqu’au XVIIe siècle.
Fonction élective, le vicomte maïeur est élu par les habitants, ni mendiants, ni étrangers, qui payent la taille, en général la veille de la Saint-Jean. Cette élection a lieu sur le parvis de l'église saint Philibert. A partir de 1669, il est permis au maire de porter "une robe longue de satin plein, de couleur violet, doublée de satin rouge cramoisi, comme le prévôt des marchands de Lyon, avec chaperon de même étoffe et couleur bordée d’hermine" afin de se distinguer des habitants.
En 1692, la fonction de vicomte maïeur est transformée en office héréditaire tandis que l’élection n’est plus alors qu’une confirmation du choix royal fait par le gouverneur au nom du roi.
Voir leur liste complète à http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liste_des_maires_de_Dijon.
François Malateste was the lawyer of the Duke of Épernon, then governor. He was appointed by Millotet, his predecessor, who wanted to be re-elected but who had been asked by the Duke of Épernon not to accept, given that the latter had promised M. the prince who did not like Millotet whom he would not accept. It bears a gules face with a gold face accompanied in chief by a gold fleur-de-lis and in base by a silver crescent. The motto on the reverse is taken from Virgil's Aeneid The mayors of Dijon From the time of the birth of feudalism, the city of Dijon had a mayor and generally twenty municipal magistrates, or aldermen. These magistrates were confirmed in 1187, when a municipal charter was granted by Duke Hugh III.. In 1192, for the first time, the mayor of Dijon was elected.
At the end of the 13th century, this mayor took the title of viscount mayor, confirmed in 1477-1479 by Louis XI, which he kept until 1789. Since the end of the 15th century (1491), the position of viscount mayor has been ennobling, as has that of alderman since the 16th century.. The Viscount Mayor had the right of high, middle and low justice, the right of seal and visitation. The keys to the city were entrusted to him and he commanded the archers as well as the companies of the seven districts, this military function being important until the 17th century..
An elective function, the Viscount Mayor is elected by the inhabitants, neither beggars nor foreigners, who pay the tax, generally on the eve of Saint John.. This election takes place on the forecourt of the Saint Philibert church. From 1669, the mayor was allowed to wear \\\"a long robe of full satin, purple in color, lined with crimson red satin, like the provost of the merchants of Lyon, with a chaperon of the same fabric and color edged with ermine\\\" in order to distinguish himself from the inhabitants..
In 1692, the function of Viscount Mayor was transformed into a hereditary office while the election was then only a confirmation of the royal choice made by the governor in the name of the king..
See their full list at http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_mayors_of_Dijon
Les maires de Dijon
Dès l’époque de la naissance de la féodalité, la ville de Dijon possédait un maire et en général vingt magistrats municipaux, ou échevins. Ces magistrats sont confirmés en 1187, lorsqu’une charte de commune est accordée par le duc Hugues III. En 1192, pour la première fois, le maire dijonnais est élu.
A la fin du XIIIe siècle, ce maire prend le titre de vicomte maïeur, confirmé en 1477-1479 par Louis XI, qu’il gardera jusqu’en 1789. Depuis la fin du XVe siècle (1491), la charge de vicomte maïeur est anoblissante ainsi que celle d’échevin à compter du XVIe siècle. Le vicomte maïeur avait le droit de haute, moyenne et basse justice, le droit de scel et de visite. Les clefs de la ville lui sont confiées et il dirige les archers ainsi que les compagnies des sept quartiers, cette fonction militaire étant importante jusqu’au XVIIe siècle.
Fonction élective, le vicomte maïeur est élu par les habitants, ni mendiants, ni étrangers, qui payent la taille, en général la veille de la Saint-Jean. Cette élection a lieu sur le parvis de l'église saint Philibert. A partir de 1669, il est permis au maire de porter "une robe longue de satin plein, de couleur violet, doublée de satin rouge cramoisi, comme le prévôt des marchands de Lyon, avec chaperon de même étoffe et couleur bordée d’hermine" afin de se distinguer des habitants.
En 1692, la fonction de vicomte maïeur est transformée en office héréditaire tandis que l’élection n’est plus alors qu’une confirmation du choix royal fait par le gouverneur au nom du roi.
Voir leur liste complète à http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Liste_des_maires_de_Dijon.
François Malateste was the lawyer of the Duke of Épernon, then governor. He was appointed by Millotet, his predecessor, who wanted to be re-elected but who had been asked by the Duke of Épernon not to accept, given that the latter had promised M. the prince who did not like Millotet whom he would not accept. It bears a gules face with a gold face accompanied in chief by a gold fleur-de-lis and in base by a silver crescent. The motto on the reverse is taken from Virgil's Aeneid The mayors of Dijon From the time of the birth of feudalism, the city of Dijon had a mayor and generally twenty municipal magistrates, or aldermen. These magistrates were confirmed in 1187, when a municipal charter was granted by Duke Hugh III.. In 1192, for the first time, the mayor of Dijon was elected.
At the end of the 13th century, this mayor took the title of viscount mayor, confirmed in 1477-1479 by Louis XI, which he kept until 1789. Since the end of the 15th century (1491), the position of viscount mayor has been ennobling, as has that of alderman since the 16th century.. The Viscount Mayor had the right of high, middle and low justice, the right of seal and visitation. The keys to the city were entrusted to him and he commanded the archers as well as the companies of the seven districts, this military function being important until the 17th century..
An elective function, the Viscount Mayor is elected by the inhabitants, neither beggars nor foreigners, who pay the tax, generally on the eve of Saint John.. This election takes place on the forecourt of the Saint Philibert church. From 1669, the mayor was allowed to wear \\\"a long robe of full satin, purple in color, lined with crimson red satin, like the provost of the merchants of Lyon, with a chaperon of the same fabric and color edged with ermine\\\" in order to distinguish himself from the inhabitants..
In 1692, the function of Viscount Mayor was transformed into a hereditary office while the election was then only a confirmation of the royal choice made by the governor in the name of the king..
See their full list at http://fr. Wikipedia. org/wiki/List_of_mayors_of_Dijon








 Cообщить об ошибке
Cообщить об ошибке Распечатать страницу
Распечатать страницу Отправить мой выбор
Отправить мой выбор Задать вопрос
Задать вопрос Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Информация
Информация















