E-auction 288-208746 - fme_412491 - NAPOLEON'S EMPIRE Médaille pour du Royaume de Westphalie
Чтобы принять участие в торгах, вы должны войти в систему и стать подтвержденным участником аукциона. Войдите, чтобы сделать ставку. Ваш аккаунт будет подтвержден в течение 48 часов. Не ждите до закрытия торгов, чтобы зарегистрироваться.Сделав ставку на данный товар, вы вступаете в юридическое соглашение на покупку выбранного товара и нажатием кнопки «Сделать ставку» подтверждаете принятие вами условий интернет-аукционов cgb.fr.
Ставка может бить сделана только в полном эквиваленте евро. Торги закроются согласно времени, указанному в описании товара, все ставки, сделанные после закрытия торгов, учитываться не будут. Не следует откладывать предложение вашей ставки до последнего момента, так как система может не успеть обработать вашу заявку, и ваша ставка не будет принята. Более детальную информацию вы найдёте здесь: FAQ по интернет-аукционам.
БЕСПЛАТНО.
БЕСПЛАТНО.
| Оценить : | 120 € |
| Цена : | 73 € |
| Максимальная предлагаемая цена : | 85 € |
| Конец торгов : | 22 October 2018 18:46:00 |
| Участников : | 4 Участников |
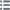
Тип Médaille pour du Royaume de Westphalie
Дата: 1807
Монетный двор / Город: Allemagne, Cassel
Металл: tin
Диаметр: 40,5 mm
Ориентация осей монеты: 12 h.
Гравер ANDRIEU Jean-Bertrand (1761-1822) / BRENET Nicolas-Guy-Antoine (1773-1846)
Вес: 10 g.
Век: lisse
Комментарии о состоянии
Médaille en bel état sur un flan de métal très léger, avec des défauts sur le bord du flan. Patine grise et brillante
Лицевая сторона
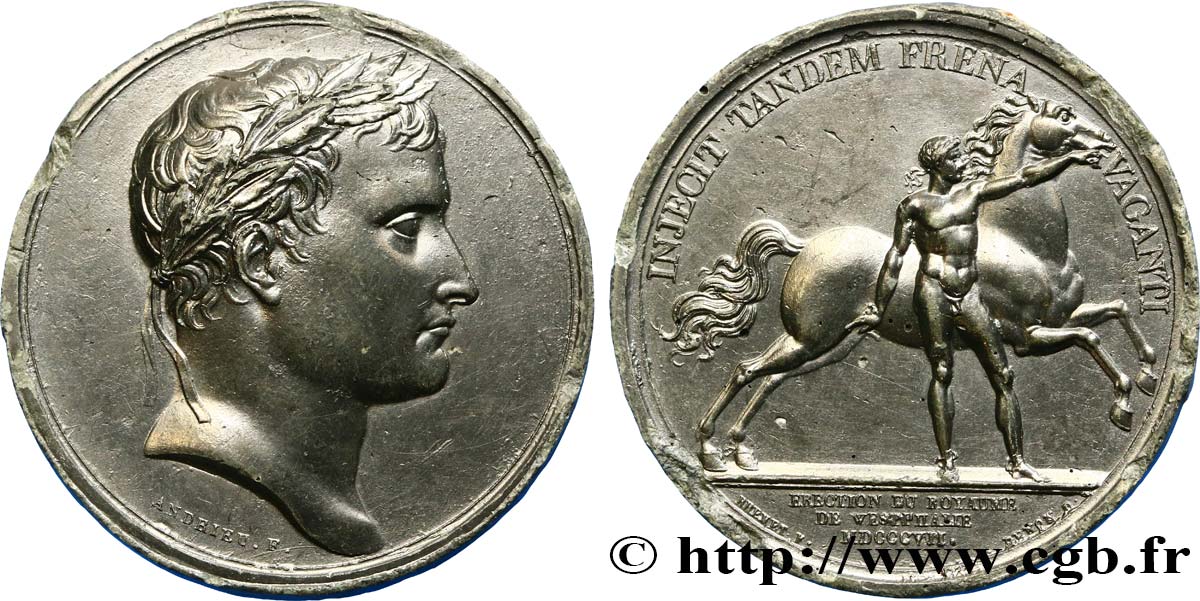
Аверс: легенда: ANÉPIGRAPHE.
Аверс: описание: Tête laurée à droite de Napoléon Ier.
Обратная сторона
Реверс: легенда: INJECIT TANDEM FRENA - VACANTI // ÉRECTION DU ROYAUME / DE WESTPHALIE / MDCCCVII.
Комментарий
Ce type de revers est aussi connu associé à d’autres droit avec le titre Napoléon Ier Empereur, au moins en 1804.
Revers signé BRENET F. DENON D. et ANDRIEU au droit.
Le royaume de Westphalie (en allemand : Königreich Westphalen) était un État membre de la Confédération du Rhin.
Déjà au début de l’année 1806, après la victoire sur la troisième coalition, Napoléon et Talleyrand envisagèrent de créer un ou deux États sur les rives du Rhin en Westphalie, composés de territoires de différents princes, dont la Prusse, qui en tant que nouvel allié de la France devait être dédommagée pour ces cessions territoriales. Par ailleurs, la Prusse se vit céder le Hanovre, fief anglais, que les Français occupaient depuis la rupture de la paix d’Amiens en 1803. Ces projets initiaux expliquent probablement le nom donné au royaume créé en 1807. Après le revirement de la politique prussienne et l’éclatement de la guerre, les armées de Napoléon occupèrent une grande partie de la Prusse et les États de ses alliés que furent le duché de Brunswick et l’Electorat de Hesse. Pendant les négociations d’armistice après la bataille d'Iéna, Napoléon comptait laisser à la Prusse certaines provinces sur la rive gauche de l’Elbe, telles que le duché de Magdebourg et la Vieille Marche mais le roi de Prusse, tablant sur le soutien efficace de son allié russe, se rétracta et la guerre se poursuivit. Après la bataille d’Eylau en février 1807, Napoléon semble avoir décidé d’enlever à la Prusse toutes ses provinces à l’ouest de l’Elbe et maintint cette décision après sa victoire de Friedland le 14 juin 1807 pendant les négociations de paix de Friedland. Toutes les cessions prussiennes, le duché de Brunswick, le landgraviat de Hesse et la partie méridionale du Hanovre furent intégrés dans le nouveau royaume de Westphalie. Cet État, nettement plus grand qu’initialement prévu et s’étendant beaucoup plus à l’est, devait servir de barrière contre la Prusse devenue l’ennemie impitoyable. Le royaume de Westphalie fut formé par Napoléon Ier en 1807, dans le but d'offrir au reste de l'Allemagne le modèle d'un État constitué d'après les principes essentiels de la Révolution française.
À cause de la dissolution du Saint-Empire romain germanique par Napoléon en 1806, Cassel devient la capitale du nouveau royaume de Westphalie : l'Empereur en donne le trône à son jeune frère, Jérôme Bonaparte. Ce dernier tient en son Château Wilhelmshöhe, devenu « Napoleonshöhe », une cour brillante. Ce royaume ne survit pas à la défaite de Leipzig en 1813..
This type of reverse is also known associated with other rights with the title Napoleon I Emperor, at least in 1804.
Reverse signed BRENET F. DENON D. and ANDRIEU to the obverse.
The Kingdom of Westphalia (German: Königreich Westphalen) was a member state of the Confederation of the Rhine.
Already at the beginning of 1806, after the victory over the Third Coalition, Napoleon and Talleyrand considered creating one or two states on the banks of the Rhine in Westphalia, consisting of territories of different princes, including Prussia, which as a new ally of France was to be compensated for these territorial cessions.. Furthermore, Prussia was ceded Hanover, an English stronghold, which the French had occupied since the breaking of the Peace of Amiens in 1803.. These initial projects probably explain the name given to the kingdom created in 1807. After the reversal of Prussian policy and the outbreak of war, Napoleon's armies occupied a large part of Prussia and the states of its allies, the Duchy of Brunswick and the Electorate of Hesse.. During the armistice negotiations after the Battle of Jena, Napoleon intended to leave to Prussia certain provinces on the left bank of the Elbe, such as the Duchy of Magdeburg and the Old March, but the King of Prussia, counting on the effective support of his Russian ally, backed out and the war continued.. After the Battle of Eylau in February 1807, Napoleon appears to have decided to take all of Prussia's provinces west of the Elbe and maintained this decision after his victory at Friedland on 14 June 1807 during the Friedland peace negotiations.. All Prussian cessions, the Duchy of Brunswick, the Landgraviate of Hesse and the southern part of Hanover were incorporated into the new Kingdom of Westphalia.. This state, significantly larger than initially planned and extending much further east, was to serve as a barrier against Prussia, which had become the ruthless enemy.. The Kingdom of Westphalia was formed by Napoleon I in 1807, with the aim of offering the rest of Germany a model of a state constituted according to the essential principles of the French Revolution..
Due to the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire by Napoleon in 1806, Kassel became the capital of the new Kingdom of Westphalia: the Emperor gave the throne to his younger brother, Jérôme Bonaparte.. The latter held a brilliant court in his Wilhelmshöhe Castle, which became the \\\"Napoleonshöhe\\\".. This kingdom did not survive the defeat at Leipzig in 1813..
Revers signé BRENET F. DENON D. et ANDRIEU au droit.
Le royaume de Westphalie (en allemand : Königreich Westphalen) était un État membre de la Confédération du Rhin.
Déjà au début de l’année 1806, après la victoire sur la troisième coalition, Napoléon et Talleyrand envisagèrent de créer un ou deux États sur les rives du Rhin en Westphalie, composés de territoires de différents princes, dont la Prusse, qui en tant que nouvel allié de la France devait être dédommagée pour ces cessions territoriales. Par ailleurs, la Prusse se vit céder le Hanovre, fief anglais, que les Français occupaient depuis la rupture de la paix d’Amiens en 1803. Ces projets initiaux expliquent probablement le nom donné au royaume créé en 1807. Après le revirement de la politique prussienne et l’éclatement de la guerre, les armées de Napoléon occupèrent une grande partie de la Prusse et les États de ses alliés que furent le duché de Brunswick et l’Electorat de Hesse. Pendant les négociations d’armistice après la bataille d'Iéna, Napoléon comptait laisser à la Prusse certaines provinces sur la rive gauche de l’Elbe, telles que le duché de Magdebourg et la Vieille Marche mais le roi de Prusse, tablant sur le soutien efficace de son allié russe, se rétracta et la guerre se poursuivit. Après la bataille d’Eylau en février 1807, Napoléon semble avoir décidé d’enlever à la Prusse toutes ses provinces à l’ouest de l’Elbe et maintint cette décision après sa victoire de Friedland le 14 juin 1807 pendant les négociations de paix de Friedland. Toutes les cessions prussiennes, le duché de Brunswick, le landgraviat de Hesse et la partie méridionale du Hanovre furent intégrés dans le nouveau royaume de Westphalie. Cet État, nettement plus grand qu’initialement prévu et s’étendant beaucoup plus à l’est, devait servir de barrière contre la Prusse devenue l’ennemie impitoyable. Le royaume de Westphalie fut formé par Napoléon Ier en 1807, dans le but d'offrir au reste de l'Allemagne le modèle d'un État constitué d'après les principes essentiels de la Révolution française.
À cause de la dissolution du Saint-Empire romain germanique par Napoléon en 1806, Cassel devient la capitale du nouveau royaume de Westphalie : l'Empereur en donne le trône à son jeune frère, Jérôme Bonaparte. Ce dernier tient en son Château Wilhelmshöhe, devenu « Napoleonshöhe », une cour brillante. Ce royaume ne survit pas à la défaite de Leipzig en 1813..
This type of reverse is also known associated with other rights with the title Napoleon I Emperor, at least in 1804.
Reverse signed BRENET F. DENON D. and ANDRIEU to the obverse.
The Kingdom of Westphalia (German: Königreich Westphalen) was a member state of the Confederation of the Rhine.
Already at the beginning of 1806, after the victory over the Third Coalition, Napoleon and Talleyrand considered creating one or two states on the banks of the Rhine in Westphalia, consisting of territories of different princes, including Prussia, which as a new ally of France was to be compensated for these territorial cessions.. Furthermore, Prussia was ceded Hanover, an English stronghold, which the French had occupied since the breaking of the Peace of Amiens in 1803.. These initial projects probably explain the name given to the kingdom created in 1807. After the reversal of Prussian policy and the outbreak of war, Napoleon's armies occupied a large part of Prussia and the states of its allies, the Duchy of Brunswick and the Electorate of Hesse.. During the armistice negotiations after the Battle of Jena, Napoleon intended to leave to Prussia certain provinces on the left bank of the Elbe, such as the Duchy of Magdeburg and the Old March, but the King of Prussia, counting on the effective support of his Russian ally, backed out and the war continued.. After the Battle of Eylau in February 1807, Napoleon appears to have decided to take all of Prussia's provinces west of the Elbe and maintained this decision after his victory at Friedland on 14 June 1807 during the Friedland peace negotiations.. All Prussian cessions, the Duchy of Brunswick, the Landgraviate of Hesse and the southern part of Hanover were incorporated into the new Kingdom of Westphalia.. This state, significantly larger than initially planned and extending much further east, was to serve as a barrier against Prussia, which had become the ruthless enemy.. The Kingdom of Westphalia was formed by Napoleon I in 1807, with the aim of offering the rest of Germany a model of a state constituted according to the essential principles of the French Revolution..
Due to the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire by Napoleon in 1806, Kassel became the capital of the new Kingdom of Westphalia: the Emperor gave the throne to his younger brother, Jérôme Bonaparte.. The latter held a brilliant court in his Wilhelmshöhe Castle, which became the \\\"Napoleonshöhe\\\".. This kingdom did not survive the defeat at Leipzig in 1813..








 Cообщить об ошибке
Cообщить об ошибке Распечатать страницу
Распечатать страницу Отправить мой выбор
Отправить мой выбор Задать вопрос
Задать вопрос Consign / sell
Consign / sell
 Информация
Информация















